In the ever-evolving landscape of real estate technology, one acronym has been gaining significant traction: IBMS. But what exactly is the IBMS full form in real estate, and why is it becoming increasingly crucial for property owners, managers, and developers? Let’s dive deep into the world of Integrated Building Management Systems and explore how they’re transforming the way we interact with our built environments.
Table of Contents
Understanding the IBMS Full Form in Real Estate
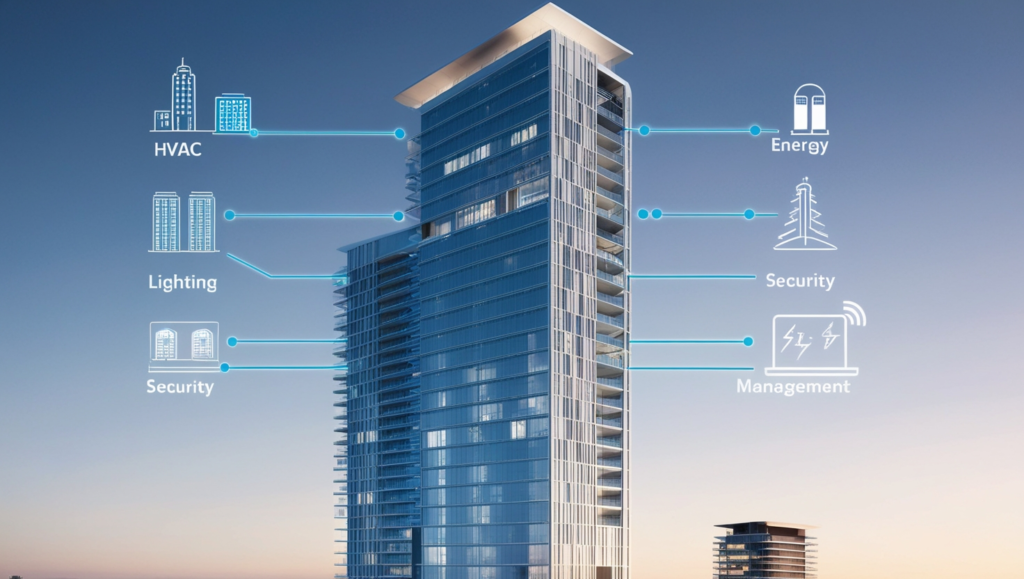
IBMS stands for Integrated Building Management System. This sophisticated network of interconnected hardware and software components is designed to oversee and control a building’s mechanical, electrical, and environmental systems. Essentially, IBMS full form in real estate represents a central nervous system for buildings, optimizing operations for efficiency, comfort, and safety.
The Core Components of an IBMS
To fully grasp the concept of IBMS full form in real estate, it’s essential to understand its key components:
Sensors: The Eyes and Ears of IBMS
Sensors are the data-gathering workhorses of an IBMS. They collect information on various parameters such as:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Occupancy
- Energy consumption
- Air quality
These sensors provide real-time data that forms the foundation of intelligent building management.

Controllers: The Brain of the System
Controllers process the data collected by sensors and make adjustments to building systems accordingly. They act as the decision-making center of the IBMS, interpreting information and issuing commands to maintain optimal building performance.
Actuators: Taking Action
Actuators are the muscles of an IBMS. They carry out commands from controllers, performing actions such as:
- Opening or closing valves
- Adjusting HVAC settings
- Activating or deactivating lighting
- Controlling access points
Human Interface: The User Experience
The human interface is where building managers and occupants interact with the IBMS. This includes:
- Display screens
- Touchscreen panels
- Software applications
- Mobile apps
These interfaces allow users to monitor, control, and customize building systems to their preferences.
Network Infrastructure: The Nervous System
The network infrastructure connects all components of the IBMS, enabling seamless communication between sensors, controllers, actuators, and human interfaces. This robust communication network is crucial for the system’s effectiveness.
Functions of IBMS in Real Estate
Now that we’ve covered the components, let’s explore the primary functions of IBMS full form in real estate:
Energy Management: Optimizing Consumption
One of the most significant benefits of IBMS is its ability to optimize energy consumption. This is achieved through:
- Intelligent lighting control based on occupancy and natural light levels
- HVAC optimization considering factors like weather, occupancy, and time-of-use pricing
- Real-time energy usage monitoring to identify areas for improvement
- Integration with renewable energy sources for maximum efficiency
Environmental Control: Creating Comfortable Spaces
IBMS plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal indoor environments:
- Temperature regulation for consistent comfort
- Humidity control to prevent mold growth and ensure occupant well-being
- Air quality monitoring and management, including CO2 levels and pollutants
- Ventilation optimization to ensure fresh air circulation
Security and Access Control: Enhancing Safety
In the realm of real estate, security is paramount. IBMS full form in real estate includes robust security features:
- Integration with CCTV systems for comprehensive surveillance
- Access control management for different areas of the building
- Fire detection and suppression system coordination
- Emergency response system integration
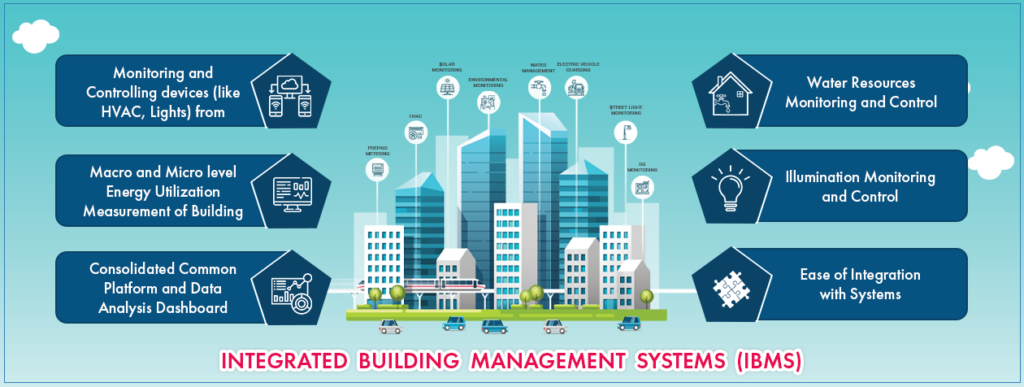
Facility Management: Streamlining Operations
IBMS significantly improves facility management processes:
- Predictive maintenance scheduling to prevent equipment breakdowns
- Asset tracking and performance monitoring
- Automated work order generation for maintenance tasks
- Space utilization analysis for optimal resource allocation
Occupant Comfort: Prioritizing User Experience
At its core, IBMS aims to enhance the comfort and satisfaction of building occupants:
- Personalized comfort settings for individual spaces
- Automated adjustments based on occupancy patterns
- Integration with smart home devices for seamless user experience
- Feedback systems for continuous improvement of comfort levels
Benefits of Implementing IBMS in Real Estate
The adoption of IBMS full form in real estate offers numerous advantages for property owners, managers, and occupants:
Significant Energy Savings
By optimizing energy consumption across all building systems, IBMS can lead to substantial reductions in energy costs. Some buildings have reported energy savings of up to 30% after implementing IBMS.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
IBMS automates many routine tasks, reducing the workload on facility management teams and allowing them to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Improved Occupant Satisfaction
With better control over environmental conditions and responsiveness to occupant needs, IBMS can significantly boost tenant satisfaction and retention rates.
Increased Property Value
Buildings equipped with IBMS are often more attractive to potential buyers or tenants, potentially increasing the property’s market value.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The wealth of data provided by IBMS enables property managers to make informed decisions about building operations, maintenance, and upgrades.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
By optimizing resource usage and reducing waste, IBMS contributes to the overall sustainability of buildings, aligning with green building certifications and environmental regulations.
Challenges in Implementing IBMS Full Form in Real Estate
While the benefits of IBMS are clear, there are some challenges to consider:
Initial Investment Costs
The upfront cost of installing an IBMS can be significant, especially for older buildings that require extensive retrofitting.
Complexity of Integration
Integrating various building systems and ensuring they communicate effectively can be a complex process, requiring specialized expertise.
Cybersecurity Concerns
As with any connected system, IBMS can be vulnerable to cyber threats. Robust security measures must be implemented to protect sensitive building data and systems.
Training and Adaptation
Building managers and occupants may require training to effectively use and benefit from IBMS features, which can be a time-consuming process.
Future Trends in IBMS for Real Estate
As technology continues to evolve, so does the potential of IBMS full form in real estate. Here are some emerging trends to watch:
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The proliferation of IoT devices is expanding the capabilities of IBMS, allowing for even more granular control and data collection within buildings.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI-powered IBMS can learn from historical data to predict and preemptively address potential issues, further optimizing building performance.
Cloud-Based IBMS Solutions
Cloud platforms are making IBMS more accessible and scalable, allowing for easier implementation and management across multiple properties.
Advanced Analytics and Visualization
Improved data analytics and visualization tools are helping property managers extract more actionable insights from the vast amount of data collected by IBMS.
Integration with Smart City Infrastructure
As smart city initiatives grow, IBMS will play a crucial role in connecting buildings with wider urban systems for improved efficiency and sustainability.
-
What is the full form of IBMS in real estate?
IBMS stands for Integrated Building Management System in real estate.
-
How does IBMS contribute to building security?
IBMS enhances building security by integrating with CCTV systems, managing access control, and coordinating emergency response systems.
-
Can IBMS be installed in existing buildings?
Yes, IBMS can be retrofitted into existing buildings, although it may require more extensive work compared to installation in new constructions.
-
What are the main components of an IBMS?
The main components of an IBMS include sensors, controllers, actuators, human interfaces, and network infrastructure.
-
How does IBMS improve energy efficiency in buildings?
IBMS improves energy efficiency by optimizing HVAC and lighting systems, monitoring energy usage, and adjusting operations based on occupancy and environmental factors.
Conclusion
The IBMS full form in real estate – Integrated Building Management System – represents a paradigm shift in how we conceptualize and manage properties. By seamlessly integrating various building systems and providing unprecedented levels of control and insight, IBMS is set to become an indispensable tool in the real estate industry.
As we move towards smarter, more sustainable cities, the role of IBMS in shaping our built environment will only grow in importance. Property owners and managers who embrace this technology now will be well-positioned to meet the evolving demands of tenants, regulatory bodies, and the environment itself.
We’d love to hear your thoughts on the future of IBMS in real estate. Have you had experience with these systems? What potential benefits or challenges do you foresee? Share your insights in the comments below and join the conversation about the future of smart buildings!