In recent years, the construction industry has witnessed a paradigm shift with the advent of 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies. This groundbreaking approach is transforming the way we build, offering solutions to longstanding challenges in the construction sector.
From reducing construction time and costs to enabling unprecedented design flexibility, 3D printing is paving the way for a more efficient and sustainable future in architecture and construction.
The Rise of 3D-Printed Homes and Innovative Construction Technologies
3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies have emerged as a game-changer in the construction industry. This revolutionary method uses large-scale 3D printers to create structures layer by layer, following digital designs with remarkable precision.
The technology has rapidly evolved from a concept to a practical reality, with numerous projects being completed around the world.
Understanding the 3D Printing Process in Construction
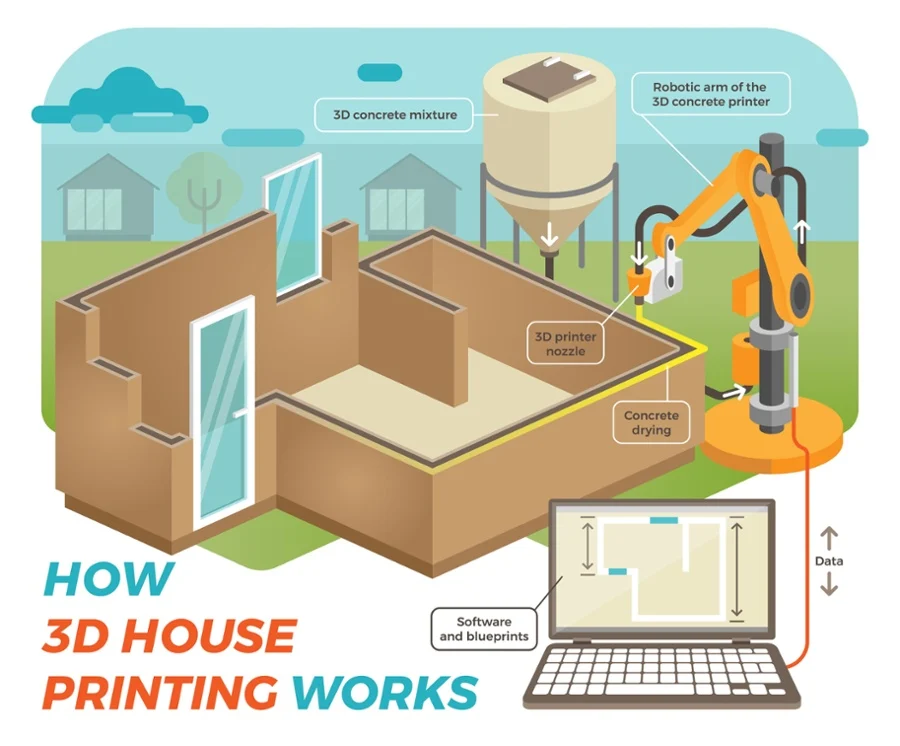
The process of creating 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies involves several key steps:
- Digital Design: Architects and engineers create detailed 3D models using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) or Building Information Modeling (BIM) software. These digital blueprints serve as the foundation for the entire construction process, allowing for precise planning and optimization.
- Material Preparation: Special concrete mixtures or other printable materials are prepared to meet the specific requirements of 3D printing. These materials must have the right consistency and curing properties to ensure structural integrity and durability.
- Printing Process: Large-scale 3D printers, often using gantry systems or robotic arms, extrude the prepared material layer by layer according to the digital design. This process can be continuous or segmented, depending on the size and complexity of the structure.
- Curing and Finishing: Once printed, the structure undergoes curing to strengthen the material, followed by finishing touches such as installing windows, doors, and utilities. This stage also includes any necessary surface treatments or additional structural reinforcements.
Historical Context and Technological Evolution
The concept of 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies has its roots in the broader field of additive manufacturing, which began to gain traction in the 1980s. However, it wasn’t until the early 2000s that researchers and engineers started exploring the possibility of scaling up 3D printing technology for construction purposes.
Key milestones in the development of 3D-printed construction include:
- 2004: Dr. Behrokh Khoshnevis at the University of Southern California introduces Contour Crafting, one of the first large-scale 3D printing technologies for construction.
- 2014: The Chinese company WinSun completes the world’s first 3D-printed houses, showcasing the potential for rapid, low-cost housing construction.
- 2018: The first family in France moves into a 3D-printed home, marking a significant step towards mainstream adoption of the technology.
- 2021: The world’s first 3D-printed school is completed in Malawi, demonstrating the technology’s potential for addressing global housing and infrastructure challenges.
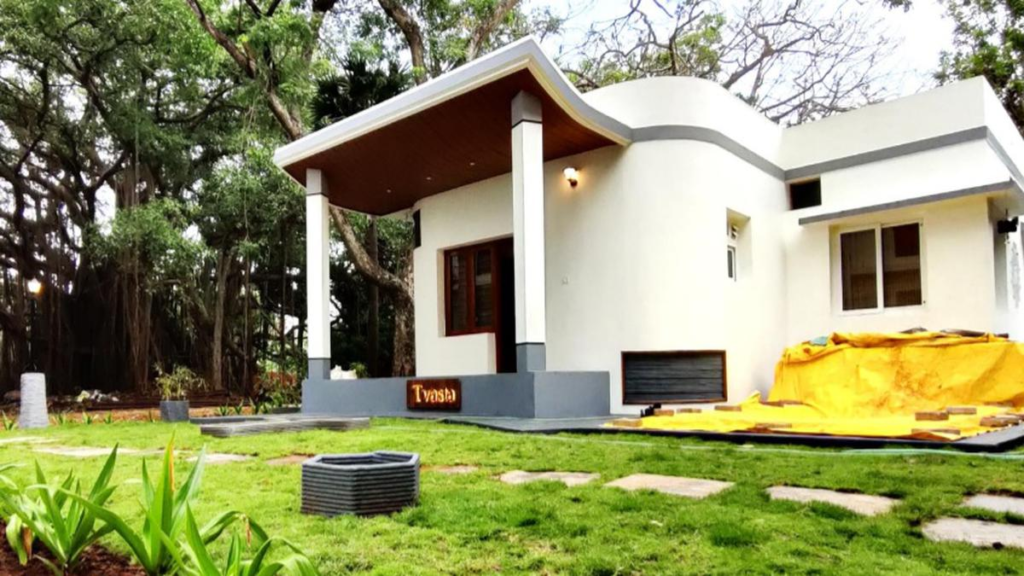

Benefits of 3D-Printed Homes and Innovative Construction Technologies
The adoption of 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies offers numerous advantages over traditional construction methods:
1. Reduced Construction Time
One of the most significant benefits of 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies is the dramatic reduction in construction time. Traditional building methods can take months or even years to complete a structure, whereas 3D printing can produce a home in a matter of days or weeks. This rapid construction process not only saves time but also reduces labor costs and minimizes disruptions to surrounding areas.
The speed of 3D printing in construction is particularly advantageous in scenarios such as:
- Disaster relief efforts, where rapid housing solutions are crucial
- Urban development projects with tight deadlines
- Remote or challenging construction sites where minimizing on-site time is beneficial
2. Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in 3D printing equipment can be substantial, the overall cost savings in the long run are significant. 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies reduce labor costs, minimize material waste, and shorten the construction timeline, all of which contribute to lower overall project expenses. As the technology continues to evolve and become more widespread, these cost savings are expected to increase further.
Cost savings are realized through:
- Reduced labor requirements, as much of the construction process is automated
- Minimized material waste, as 3D printing uses only the necessary amount of material
- Shorter project timelines, reducing overhead costs and enabling faster return on investment
- Potential for using lower-cost, locally sourced materials
3. Design Flexibility and Customization
3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies offer unprecedented design freedom, allowing architects to create complex and unique structures that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. The technology enables the realization of curved walls, intricate patterns, and unconventional shapes with ease. This level of customization allows homeowners to have truly personalized living spaces tailored to their specific needs and preferences.
Examples of design possibilities include:
- Organic, curved structures that blend seamlessly with natural surroundings
- Intricate facade designs and textures that would be cost-prohibitive with traditional methods
- Customized interior layouts optimized for specific lifestyles or accessibility needs
- Integration of complex geometric patterns for both aesthetic and functional purposes
4. Sustainability and Reduced Environmental Impact
The construction industry is known for its significant environmental footprint, but 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies are helping to address this issue.
The precision of 3D printing minimizes material waste, and the ability to use eco-friendly materials such as recycled plastics or locally sourced natural materials further reduces the environmental impact. Additionally, the reduced need for transportation of materials and shorter construction times contribute to lower carbon emissions.
Sustainability benefits include:
- Reduced material waste, as 3D printing uses only the necessary amount of material
- Potential for using recycled or sustainable materials in the printing process
- Lower carbon emissions due to reduced transportation and shorter construction times
- Improved energy efficiency through optimized designs and material choices
- Potential for easier deconstruction and material recycling at the end of a building’s life cycle
5. Improved Safety and Working Conditions
Construction sites can be hazardous environments, but 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies help mitigate many of these risks. By automating much of the construction process, workers are less exposed to dangerous situations such as working at heights or handling heavy materials. This not only improves safety but also addresses labor shortages in the construction industry.
Safety improvements include:
- Reduced need for workers to operate in hazardous conditions
- Minimized risk of injuries associated with manual labor and heavy machinery
- Improved quality control through automated processes, reducing the risk of structural defects
- Potential for 24/7 construction operations without compromising worker safety
Challenges and Considerations for 3D-Printed Homes and Innovative Construction Technologies
While the potential of 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies is immense, there are several challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption:
1. Regulatory Hurdles
As with any new technology, 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies face regulatory challenges. Building codes and standards need to be updated to accommodate this new construction method, ensuring that 3D-printed structures meet safety and quality requirements. Many countries are working on developing specific regulations for 3D-printed buildings, but progress varies globally.
Key regulatory considerations include:
- Establishing performance standards for 3D-printed structures
- Developing testing and certification processes for new materials and printing methods
- Updating zoning laws and building codes to accommodate 3D-printed homes
- Addressing liability and insurance issues related to this new construction method
2. Material Limitations
While concrete mixtures are commonly used in 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies, ongoing research is exploring a wider range of printable materials. Developing materials that are strong, durable, and suitable for various climates and building requirements is crucial for the widespread adoption of this technology.
Current material challenges include:
- Ensuring consistent material properties throughout the printing process
- Developing materials with appropriate curing times and structural strength
- Creating eco-friendly material options that meet construction standards
- Addressing the need for reinforcement in larger structures
3. Scale and Size Limitations
Current 3D printing technology has limitations in terms of the size of structures that can be printed. While smaller homes and buildings are readily achievable, printing larger structures or multi-story buildings presents challenges that researchers and engineers are actively working to overcome.
Scaling challenges include:
- Developing larger 3D printers capable of constructing taller buildings
- Ensuring structural integrity and stability in larger 3D-printed structures
- Addressing logistical challenges of on-site printing for large-scale projects
- Integrating traditional construction methods with 3D printing for complex structures
4. Public Perception and Acceptance
As with any new technology, there may be skepticism or hesitation from the public regarding 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies. Educating potential homeowners, investors, and industry professionals about the benefits and safety of 3D-printed structures is essential for widespread acceptance.
Factors influencing public perception include:
- Aesthetic considerations and the “look” of 3D-printed homes
- Concerns about the long-term durability and maintenance of 3D-printed structures
- Cultural and social acceptance of non-traditional construction methods
- Awareness of the environmental and economic benefits of 3D printing in construction
Global Adoption of 3D-Printed Homes and Innovative Construction Technologies
The adoption of 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies is gaining momentum worldwide, with various countries and regions leading the way:
Europe: Pioneering Research and Development
European countries, particularly the Netherlands, Germany, and Denmark, are at the forefront of research and development in 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies. These nations have completed several successful projects and are actively working on refining the technology for broader applications.
Notable European projects include:
- The 3D-printed bridge in Amsterdam, showcasing the technology’s potential for infrastructure
- The BOD (Building on Demand) project in Copenhagen, demonstrating the feasibility of on-site 3D printing
- Multiple 3D-printed housing projects in Italy, exploring various designs and materials
North America: Addressing Housing Challenges
In the United States, companies like ICON are using 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies to address affordable housing challenges. Projects in Texas and Mexico have demonstrated the potential of 3D printing to provide quick and cost-effective housing solutions.
Key developments in North America include:
- ICON’s partnership with New Story to create a 3D-printed community in Mexico
- The first permitted 3D-printed home in Austin, Texas, setting a precedent for future projects
- Ongoing research at universities and national laboratories to advance 3D printing technologies
Asia and the Middle East: Ambitious Projects and Government Support
Countries like China and the United Arab Emirates are embracing 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies with ambitious projects. Dubai, for example, aims to have 25% of new buildings constructed using 3D printing by 2030, showcasing the technology’s potential on a large scale.
Significant developments in Asia and the Middle East include:
- The world’s tallest 3D-printed building in Suzhou, China, standing at 5 stories
- Dubai’s 3D-printed office building, demonstrating the technology’s application in commercial structures
- Saudi Arabia’s plans to use 3D printing in its NEOM megacity project
The Future of 3D-Printed Homes and Innovative Construction Technologies
As 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see several exciting developments:
1. Integration with Smart Home Technology
Future 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies are likely to seamlessly integrate smart home features, allowing for more efficient energy management, improved security, and enhanced living experiences. This integration could include:
- Embedded sensors and smart systems printed directly into the structure
- Optimized layouts for energy efficiency and smart device integration
- Customizable home automation features tailored to individual user needs
2. Multi-Material Printing
Advancements in 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies may lead to the ability to print with multiple materials simultaneously, enabling the creation of more complex and functional structures. This could revolutionize construction by:
- Combining structural and insulating materials in a single printing process
- Integrating electrical and plumbing systems directly into the printed structure
- Creating gradient materials with varying properties throughout the building
3. Off-World Construction
As space exploration continues to advance, 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies could play a crucial role in building habitats on other planets, utilizing local materials and minimizing the need for transported supplies. Potential applications include:
- Constructing lunar or Martian habitats using regolith (local soil) as a printing material
- Creating modular, expandable structures for long-term space missions
- Developing self-repairing structures capable of withstanding extreme environments
4. Disaster Relief and Emergency Housing
The speed and efficiency of 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies make them ideal for rapid deployment in disaster-stricken areas, providing quick and sturdy temporary or permanent housing solutions. Future developments could include:
- Mobile 3D printing units for on-site deployment in disaster zones
- Standardized designs for quick assembly of emergency shelters
- Integration with other technologies for rapid infrastructure restoration
5. Sustainable Urban Development
As cities grow and evolve, 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies could enable the creation of more sustainable and efficient urban environments, with buildings designed to maximize energy efficiency and minimize environmental impact. This could lead to:
- Urban renewal projects utilizing 3D printing for efficient, sustainable redevelopment
- Vertical farming integrated into 3D-printed structures for local food production
- Customized urban landscapes that blend architecture with natural ecosystems
6. Advancements in Materials Science
The future of 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies will likely see significant advancements in materials science, leading to new possibilities in construction:
- Development of self-healing materials that can repair minor damage autonomously
- Creation of adaptive materials that respond to environmental conditions
- Utilization of nanotechnology to enhance material properties and performance
Economic and Social Implications
The widespread adoption of 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies is likely to have far-reaching economic and social implications:
Job Market Transformation
While automation may reduce the need for certain traditional construction roles, it will also create new job opportunities in areas such as:
- 3D printer operation and maintenance
- Specialized design for 3D-printed structures
- Material science and development for 3D printing applications
Affordable Housing Solutions
The cost-effectiveness and speed of 3D printing could help address global housing shortages by:
- Enabling rapid construction of affordable housing in developing regions
- Providing low-cost housing options in expensive urban areas
- Facilitating the creation of transitional housing for homeless populations
Education and Skills Development
The rise of 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies will necessitate changes in education and training for the construction industry:
- Integration of 3D printing technologies into architectural and engineering curricula
- Development of specialized training programs for 3D printing technicians
- Continuing education for existing construction professionals to adapt to new technologies
Conclusion
3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies represent a significant leap forward in the construction industry. By offering faster construction times, reduced costs, enhanced design flexibility, and improved sustainability, this technology has the potential to revolutionize how we build and live in our homes and cities.
As research continues and the technology matures, we can expect to see even more exciting applications and advancements in the field of 3D-printed construction.
The future of construction is being shaped by these innovative technologies, and it’s an exciting time for architects, engineers, and homeowners alike. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with 3D-printed homes and innovative construction technologies in the comments below.
Have you seen a 3D-printed structure in person? What potential applications of this technology are you most excited about? Join the conversation and let’s explore the future of construction together!